Gas Limits: A Beginner's Guide on Optimizing Your Transaction Fees
Gas limits and gas prices decide whether a crypto transaction succeeds, fails, or gets stuck waiting. This guide breaks down what those numbers actually mean, how fees are calculated, and how to avoid paying for transactions that don’t go through.

Key Takeaways
- Gas limits set the maximum computational work your transaction can do. Gas prices decide how much you pay per unit of that work.
- Set the gas limit too low and your transaction fails while still costing you fees. Set it too high and it won’t cost more, but it can temporarily lock up funds.
- Wallets usually estimate gas correctly, but with KAST, you don’t have to think about gas at all, transactions are fast, predictable, and cheap.
You’re about to send crypto. You confirm the transaction. Then you see this:
Gas Limit: 21,000
Gas Price: 50 gwei
And you think: okay… but what am I actually agreeing to?
If you’ve ever paid a fee for a transaction that didn’t go through, congrats, you’ve already learned about gas limits the annoying way.
If you’ve ever watched a transaction sit there for hours while you refresh the page like it’s going to help, that was the gas price.
This guide explains what gas limits are, how gas prices work, and how KAST simplifies the process for you.
The Two Numbers You See Before You Send
Every time you send a transaction, you’re making two decisions:
- Gas limit → how much work your transaction is allowed to do
- Gas price → how much you’re willing to pay per unit of work
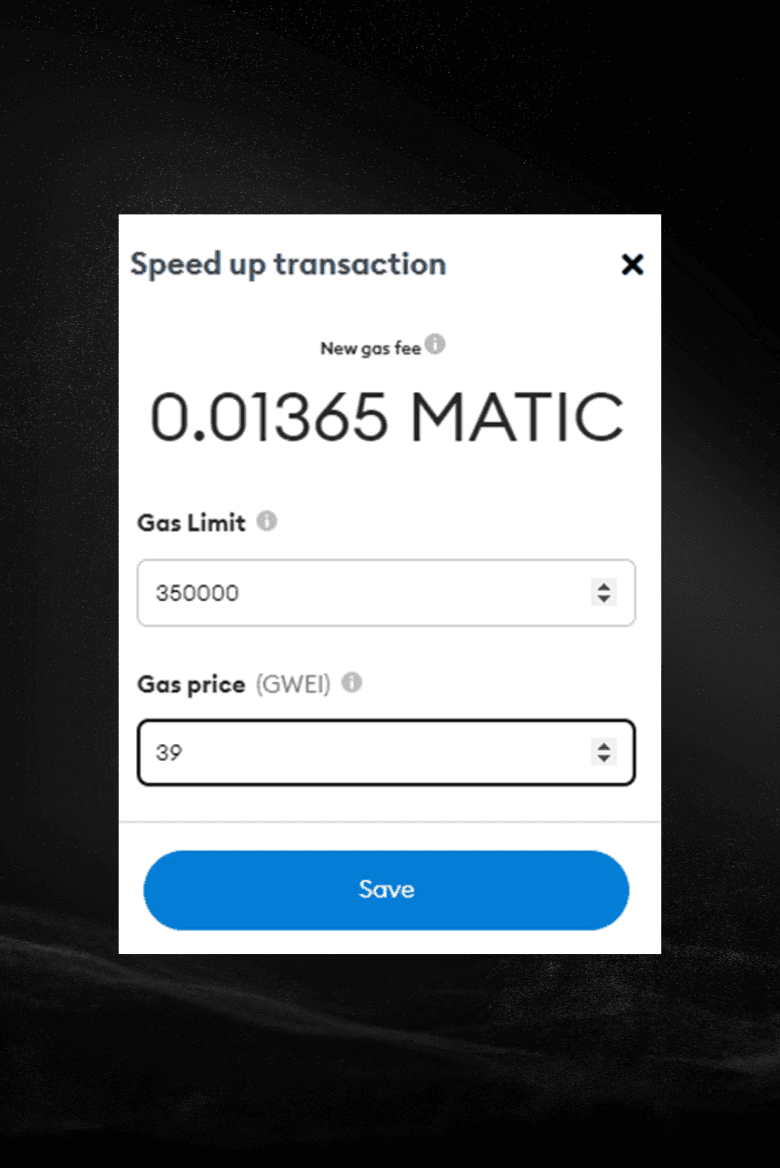
One controls whether the transaction can finish.
The other controls how fast it gets processed.
Mix those up and things get expensive or slow. Sometimes both.
How Gas Fees Are Actually Calculated
Here’s the rule everything else builds on:
Total transaction fee = gas used × gas price
Important details:
- You’re only charged for the gas actually used
- The gas limit is a cap, not a bill
- If the transaction runs out of gas before finishing, it fails, and the gas spent is gone
Keep this formula in mind. It explains almost every gas-related issue you’ll run into.
Gas Limit: How Much Work Your Transaction Can Do
Every blockchain action requires computation. The amount of work depends on what you’re doing.
Sending ETH takes minimal effort. It’s a simple transfer from one address to another.
Swapping tokens involves more steps. The transaction has to interact with smart contracts, calculate prices, and update balances.
Minting an NFT takes even more work, since it creates new data on-chain and often triggers multiple contract actions.
The gas limit is you saying, “This transaction can use up to this much effort.”
Why Gas Limits Exist
Gas limits protect you and the network.
They stop buggy or malicious smart contracts from running forever and draining funds. Once the limit is hit, execution stops.
How Gas Limits Are Set
Some actions have known limits:
- Simple ETH transfer: 21,000 gas
- Token swaps or DeFi actions: 100,000–300,000+ gas
Wallets usually estimate this for you based on simulations.
What Happens If the Limit Is Too Low
If the transaction hits the gas limit before finishing, it fails.
Even though your tokens don't move, you still spend gas, which is the reason why failed transactions cost money.
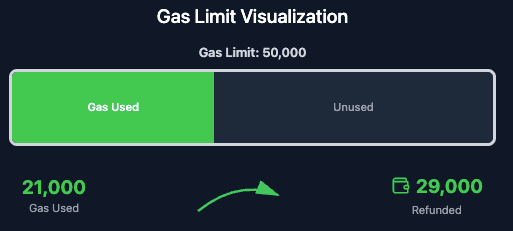
The gas limit is a cap on the maximum gas you're willing to spend. You only pay for the gas actually used during execution. Any unused gas is automatically refunded to your wallet.
What Happens If the Limit Is Too High
The transaction completes normally.
You won’t pay extra, but some wallets temporarily reserve the full gas limit amount until confirmation. On busy networks, that can tie up funds longer than necessary.
Gas Price: How Fast Your Transaction Gets Picked Up
Gas price is how much you pay per unit of gas, usually measured in gwei.
Block space is limited. Validators choose which transactions to include first.
Higher gas price = higher priority.
Lower gas price = cheaper, but slower.
The Trade-Off
- Higher price: Faster confirmation
- Lower price: Less cost, more waiting
If your transaction is slow, the issue is almost always gas price rather than gas limit.
Base Fee vs Priority Fee (Ethereum Networks)
On Ethereum and similar chains (especially its Layer-2s), gas price has two parts.
There’s the base fee, which the network sets automatically. You don’t negotiate it. Everyone in the block pays the same base fee, and it gets burned.
Then there’s the priority fee. That’s your tip. This is the part you actually control.
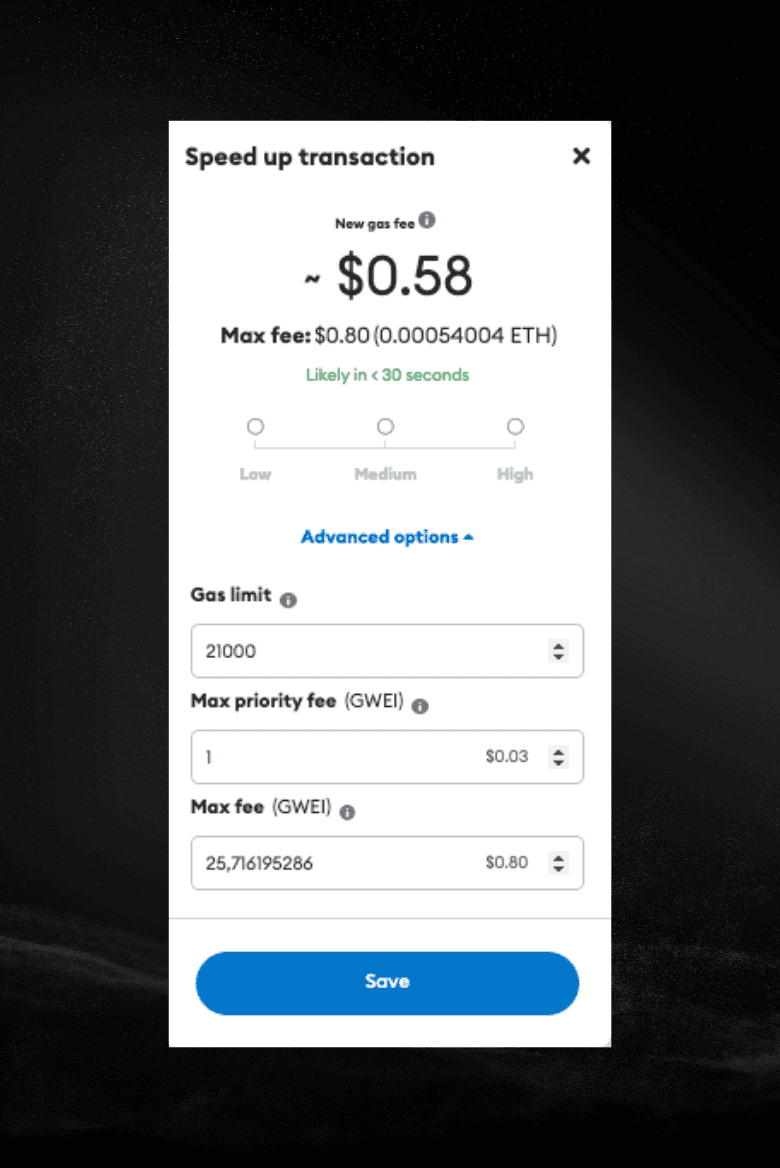
Total gas price is just the base fee plus your tip.
So when you send a transaction, you’re saying:
“I accept the current base fee, and here’s how much extra I’m willing to pay to not wait.”
Clear. No mystery.
Example
You send 1 ETH.
- Gas limit: 21,000
- Base fee: 10 gwei
- Priority fee: 5 gwei
Total gas price: 15 gwei
Gas cost: 21,000 × 15 = 315,000 gwei (0.000315 ETH)
- 1 ETH goes to the recipient
- Base fee is burned
- Validator receives the priority fee
Clear, predictable, and fully visible.
When to Adjust Gas Limit vs Gas Price
Most of the time, you leave the gas limit alone.
You adjust gas price when:
- your transaction is slow
- the network is busy
- you want it confirmed sooner rather than later
You adjust gas limit when:
- transactions keep failing
- you’re using complex contracts
- the wallet estimate looks suspiciously low
If you’re randomly tweaking both, you’re just guessing.
Modern wallets simulate transactions before sending them.
They estimate the required gas limit, show the base fee and add a reasonable priority fee.
Most of the time, the default settings work fine. Manual changes matter mainly during congestion or complex interactions.
What Goes Wrong When Gas Is Set Incorrectly
Nothing mysterious, just math.
High-Throughput Chains: Why Gas Feels Invisible
On networks like Solana, transactions use fixed computational budgets and extremely low fees.
You don’t set gas limits.
You don’t bid for block space.
Fees stay predictable and tiny.
That’s why transactions confirm quickly and cost fractions of a cent.
How KAST Handles Gas
When you top up or spend with KAST, transactions run on high-throughput blockchain infrastructure.
Card payments and KAST Tag transfers happen instantly with no gas fees.
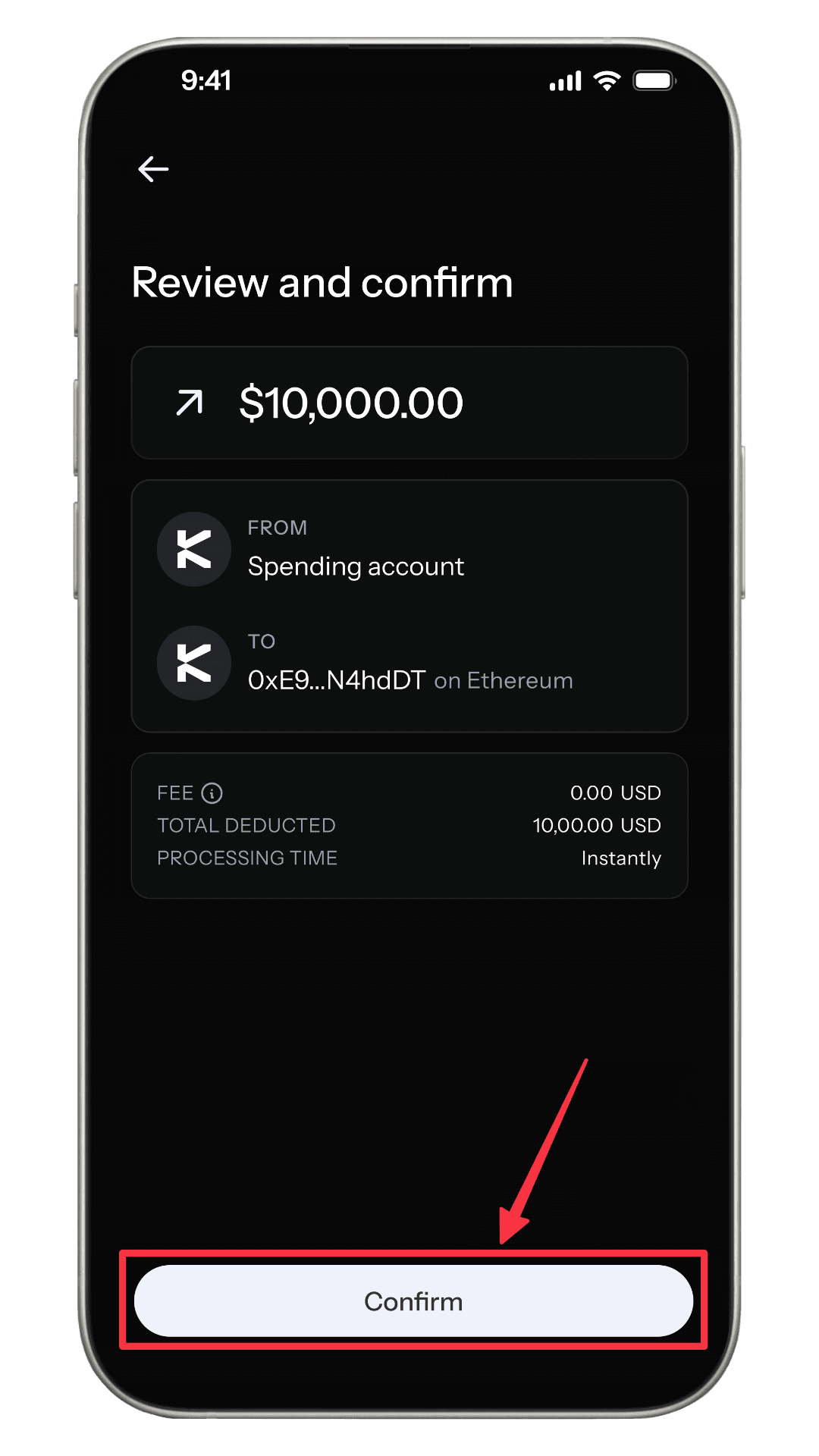
You don't choose gas limits. You don't tune fees. Transactions confirm fast and are cheap.
You don't need to think about gas to move money. That's the whole point.
Network gas fees only apply when sending to external crypto wallet addresses. Even then, KAST will handle it for you.
Putting It All Together
Gas limits cap how much work a transaction can do, while gas prices determine how quickly it gets processed by the network.
Set the limit too low and the transaction fails; set the price too low and it just sits there waiting.
Most wallets handle this automatically, but understanding what you’re looking at still matters, especially when things go sideways and you need more control.
On modern, payment-focused blockchains, that entire layer of complexity disappears.
And honestly, your money should move when you tell it to, not after a mini exam in network mechanics.
Disclaimer: This content is provided by KAST Academy for educational purposes only and is not intended as financial advice or a recommendation to engage in any transaction. All information is provided "as-is" and does not account for your individual financial circumstances. Digital assets involve significant risk; the value of your investments may fluctuate, and you may lose your principal. Some products mentioned may be restricted in your jurisdiction. By continuing to read, you agree that KAST group, KAST Academy, its directors, officers and employees are not liable for any investment decisions or losses resulting from the use of this information.
Related articles
What Are Gas Fees and Why Are They So Cheap on Solana?
Gas fees are the cost of processing transactions on a blockchain. Some networks charge dollars or more per transaction, while others charge fractions of a cent. The difference comes down to how each blockchain is designed, and why Solana makes everyday crypto spending fast and cheap.

Blockchain Confirmations Guide: ‘Instant’ Payments Aren't Always Final
Crypto payments feel instant, but finality takes time. Here’s what really happens after you hit send, why confirmations matter, and how KAST removes that friction from everyday spending.

What Stablecoins And Networks Are Supported By KAST?
Did you know KAST supports stablecoins like USDC, USDT, PYUSD, RLUSD and networks like Solana, Ethereum, Polygon, Tron, BSC, and more? Learn how to choose the right network based on transaction fees, speed, and compatibility.